Math 152B
Practice
Exam II
Please do all of the following problems. All work and all answers must be done on your own paper. Credit earned will be based on the steps that you show that lead to the final solution. Good Luck!
Problem 1 Find the root:
![]()
-2, since (-2)3 = -8
Problem 2 Simplify the expression. Leave your answer in exponential form with only positive exponents.
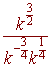
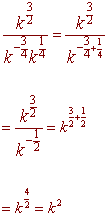
Problem 3 Multiply and Simplify
![]()
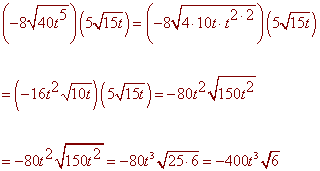
Problem 4 Simplify the expression. Assume all variables represent positive real number.
![]()
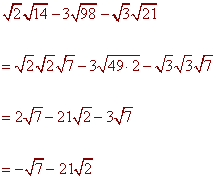
Problem 5 Multiply and Simplify
![]()
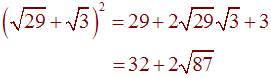
Problem 6 Rationalize the denominator
4 -
![]()
5 (4 +
![]() )
)
( 4 - ![]() )(4 +
)(4 +
![]() )
)
20 + 5![]()
=
16 - 6
20 + 5![]()
=
10
Problem
7
Simplify
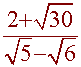
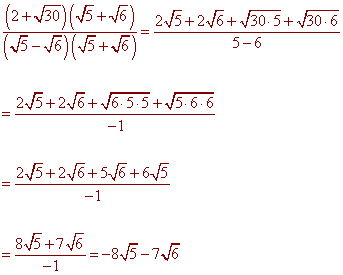
Problem 8
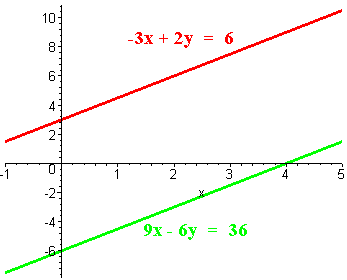
Use the method of elimination to solve the system. Then graph the system to check your solution.
-
-3x + 2y = 6
9x - 6y = 36
Solution
We multiply the first equation by 3 and add
-9x + 6y = 18
9x - 6y = 360 = 54
This is a contradiction, so there is no solution.
To graph it we have make T-Tables as shown belowx y 0 3 -2 0 x y 0 -6 4 0 The graphs are shown below. Notice that they are parallel.
-
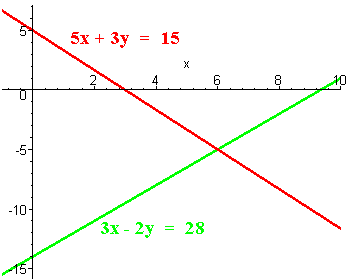
5x + 3y = 15
3x - 2y = 28
Solution
Multiply the first equation by 2 and the second by 3 and add
10x + 6y = 30
9x - 6y = 8419x = 114
x = 114/19 = 6Now substitute this value into the second equation (the first will work also) to get
3(6) - 2y = 28
18 - 2y = 28
-2y = 28 - 18 = 10
y = 10/-2 = -5
The solution is (6, -5).
To graph it we have make T-Tables as shown below
x y 0 5 3 0 x y 0 -14 28/3 0 The graphs are shown below. Notice that the lines intersect at (6,-5).
Use the method of substitution to solve the system. Then graph the system to check your solution.
-
7x + y = 3
4x + 3y = -8
Solution
We solve the first equation for y:
y = 3 - 7x
Now plug this into the second equation:
4x + 3(3 - 7x) = -8
4x + 9 - 21x = -8
9 - 17x = -8
-17x = -17
x = 1
Now plug in x = 1 in the equation
y = 3 - 7(1) = -4
Hence the solution is (1,-4).
To graph it we have make T-Tables as shown below
x y 0 3 3/7 0 x y 0 -8/3 -2 0 The graphs are shown below. Notice that the lines intersect at (1,4).
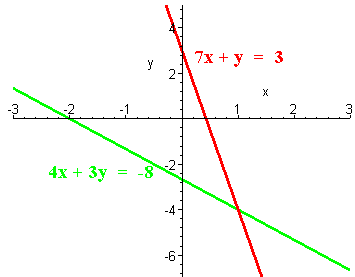
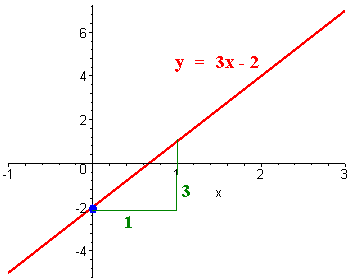
-
y = 3x - 2
6x - 2y = 4
Solution
We can substitute the first equation into the second:
6x - 2(3x - 2) = 4
6x - 6x + 4 = 4
4 = 4
This is an identity, hence there are an infinite number of solutions (all points lying on the line y = 3x - 2). Notice the the y-intercept is -2 and the slope is 3. We can draw the point (0,-2) and rise 3 and run 1 from this point to graph the line.
![]()
Square both sides:
a2 + 24 = (a - 2)2
a2 + 24 = a2 - 4a + 4
24 = -4a + 4
4a = -20
a = -5
Notice that when we plug x = -5 into the right hand side of the original equation, we get -7, while the left hand side produces 1. Hence there is no solution.
A. | 2x - 4 | + 3 > 7
Solution
First subtract 3 from both sides
|2x - 4| > 4
Now turn this into an "or" statement
2x - 4 = 4 or 2x - 4 = -4
2x = 8 or 2x = 0
x = 4 or x = 0
Now test the point x = 1 to see if we yield a true statement
|2(1) - 4| + 3 = |-2| + 3 = 2 + 3 = 5
is not greater than 7. Hence the solution is the outside two intervals:
(-
![]() , 0) U
(4,
, 0) U
(4, ![]() )
)
B. | 3x - 8 | + 5 < 4
Solution
First subtract 5 from both sides of the inequality
|3x - 8| < -1
Now notice that the absolute value can never be negative, in particular it is never less than -1. Hence there is no solution.
C. 3| x - 5| < 9
SolutionFirst divide both sides by 3 to get
|x - 5| < 3
Now turn this into an "or" equation.x - 5 = 3 or x - 5 = -3
x = 8 or x = 2
Now test a between point such as 5:|(5) - 5| = 0 which is less than 3, hence the between interval is the solution. The solution is
(2,8)Problem 12 Solve the equation
x
- 3 x - 6
-
= 0
x + 1 x +
5
Solution
Multiple all three terms by the common denominator (x + 1)(x + 5)
(x
- 3)(x + 1)(x + 5)
(x - 6)(x + 1)(x + 5)
-
= 0
x + 1 x +
5
(x - 3)(x + 5) - (x - 6)(x + 1) = 0
[x2 - 3x + 5x - 15] - [x2 - 6x + x - 6] = 0
[x2 + 2x - 15] - [x2 - 5x - 6] = 0
x2 + 2x - 15 - x2 + 5x + 6 = 0
7x - 9 = 0
7x = 9
x = 9/7
Problem 13
r
S = 1 +
m
Solution
first subtract 1 from both sides
r
S - 1 =
m
Now multiply both sides by m
m(S - 1) = r
Now divide both sides by S - 1
r
m =
S
- 1
Problem 14 Steve can paint his house in 10 hours working by himself. Working together, Anne and Steve can paint the house in just 6 hours. How long would it take Anne to paint the house by herself?
Solution
Since Steve can paint the house in 10 hours, he paints the house at the rate of 1/10 houses per hour. If Anne can paint the house in x hours, she paints at a rate of 1/x houses per hour. The sum of the individual rates equal the total rate (1/6 houses per hour).
1
1 1
+
=
10
x 6
Now multiply by the common denominator 30x
1 (30x)
1(30x) 1 (30x)
+
=
10
x
6
3x + 30 = 5x
2x = 30
x = 15
It would take Anne 15 hours to paint the house by himself.
Problem 15 Derek bicycled 36 miles to get to Echo Summit and back and Nick bicycled 60 miles to get to Carson Pass and back. Nick rode 3 miles per hour faster than Derek, and his trip took an hour longer than Derek's. What is the fastest speed that Derek could have been traveling? (You must set up the equations, that is, no guessing).
We construct the following Distance-Rate-Time table
| Distance | Rate | Time | |
| Derek | 36 | r | t |
| Nick | 60 | r + 3 | t + 1 |
This gives us the two equations
36 = rt 60 = (r + 3)(t + 1)
The first equation gives us
t = 36/r
so that
60 = (r + 3)(36/r + 1)
Multiplying both sides by r gives
60r = (r + 3)(36 + r) = r2 + 39r + 108
or
r2 - 21r + 108 = 0
(r - 9)(r - 12) = 0
So that
r = 9 or r = 12
The fastest that Derek could have been traveling is 12 miles per hour.
Problem 16 Simplify
x
3 -
x + 1
x
1
+
6
4
Solution
We first find the least common denominator. The denominators are x + 1, 6, and 4. The LCD is
LCD = 12(x + 1)
Now multiply the two terms in the numerator and the two in the denominator by the LCD
x 12(x + 1)
3(12)(x + 1) -
x + 1 1
x
12(x + 1)
1 12(x + 1)
+
6
1
4 1
Now cancel to get
3(12)(x + 1) - 12x
=
2x(x
+ 1) + 3(x + 1)
Distribute to get
36x + 36 - 12x
=
2x2 + 2x + 3x + 3
Combine like terms
24x + 36
=
2x2
+
5x + 3
Factor the numerator and the denominator
12(2x + 3)
=
(2x + 3)(x + 1)
Now cancel the x + 1 to get
12
=
x + 1
Back to the Factoring and Rational Expressions Page
Back to the Basic Algebra Part II Page
Back to the Math Department Home Page
Questions, Comments and Suggestions Email: greenl@ltcc.edu