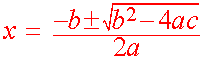The Quadratic Formula
Quadratic Formula
Lets complete the square for
ax2 + bx + c
- a(x2 + b/a x) + c
- -b
2a
- b2
4a2
-
b
b2 b2
a( x2 +
a 4a2 4a2
-
b
b2
b2
a[ ( x2 +
a 4a2 4a2
-
b
b2
a[ ( x +
2a 4a2
-
b
b2
a( x +
2a 4a
Now what if we want to solve the equation
ax2 + bx + c = 0
We can equivalently solve
b
b2
a( x +
)2 -
+ c =
0
2a
4a
by the root method
b
b2
a( x +
)2 =
-
c
2a
4a
b
b2
c
( x +
)2 =
-
2a
4a2
a
b2 - 4ac
=
4a2
Now take a square root of both sides to get
![]()
Finally subtract b/2a from both sides to get the quadratic formula.
|
The Quadratic Formula The solution to ax2 + bx + c = 0 is
|
Memorize This Formula!
Example
Solve
3x2 - 2x + 5
Solution
a = 3 b = -2 c = 5
We have
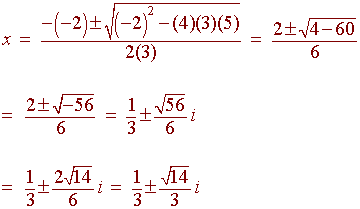
The Discriminant
We define the discriminant as
D = b2 - 4ac
is a convenient measure of determining how many real roots (solutions) there are. Notice that D is the expression inside of the square root sign in the quadratic formula. Since the square root of a negative number produces only complex numbers, we see that if D is negative, then there will be no real roots. If D is a positive number, then the quadratic formula will produce two roots (one for the plus and one for the minus). If D is 0 then plus 0 and minus 0 are the same number, so we get only one root. The table below summarizes.
| D | Number of Real Roots |
| Positive | 2 |
| Negative | 0 |
| Zero | 1 |
Example:
How many roots are there for the equation:
3x2 - 5x + 1 = 0
We have
D = 25 - 12 > 0
hence there are two real roots.
The Sum and Product of the Roots
Since the two roots of a quadratic are
![]()
and
![]()
then if we add the two roots, we get:
![]()
and if we multiply the two roots we get
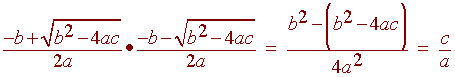
Note that if a is 1 then the sum of the roots is -b and the product is c. This relates to factoring when we find two numbers that add to b and multiply to c.
Example
What are the sum and product of the roots of
4x2 -3x + 2
Solution
The sum is
b 3
-
=
a 4
and the product of the roots is
c
2 1
=
=
a
4 2
Determining the Quadratic Equation From the Roots
If we know the roots of a quadratic then it is easy to find the original quadratic by using the zero product formula in reverse.
Example
Find an equation of a quadratic that has roots 2 and -4/3.
Solution
We can write:
(x - 2)(x - (-4/3)) = (x - 2)(x + 4/3)
4
8
2 8
= x2 +
x - 2x - =
x2 - x -
3
3
3 3
Exercise:
Find a quadratic with the following roots
-
0 and -1/2

-
3 -
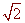 and 3 +
and 3 +
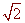

-
4 + i and 4 - i

Back to the Quadratic Functions and Linear Inequalities Page
Back to the Basic Algebra Part II Page