Functions of Two Variables
I. Homework
II. Planes
Recall that a line is given by the first degree polynomial ax +by = c
similarly, a plane is given by the first degree polynomial ax + by + cz = d
to graph a plane, plot the x, y, and z intercepts.
Example: Sketch the graph of the plane 2x + 3y + z = 6
We find the x intercept by setting y and z =0, 2x = 6 or x = 3 the x-intercept is
(3,0,0)
Similarly, the y intercept is (0,2,0) and the z intercept is (0,0,6). Now plot the three points and connect the three points to sketch a triangle that sits in the plane.
IV. Quadric Surfaces
Recall that the quadrics or conics are lines , hyperbolas, parabolas, circles, and ellipses. In three dimensions, we can combine any two of these and make a quadric surface. For example
z = x2 + y2
is a paraboloid since for constant z we get a circle and for constant x or y we get a parabola. We use the suffix -oid to mean ellipse or circle. We have:
x2/a2 + y2/b2 + z2/c2 = 1 is an ellipsiod
-x2/a2 - y2/b2 + z2/c2 = 1 is a hyperboloid of 2 sheets while
x2/a2 + y2/b2 - z2/c2 = 1 is a hyperboloid of 1 sheet
III. Definition of Functions of Several Variables
A function of several variables is a function where the domain is a subset of Rn and range is R.
Example:
f(x,y) = x - y is a function of two variables
g(x,y,z) = (x - y)/(y - z)
is a function of three variables.
IV. Finding the Domain
To find the domain of a function of several variables, we look for zero denominators and negatives under square roots:
Example
Find the domain of f(x,y) = sqrt(x - y)/(x + y)
The first we have x - y > 0
second we have x + y not= 0 hence we need to stay off the line y = -x
The domain is {(x,y)| x - y > 0 and y not= -x}
Exercise
Find the domain of the function f(x,y,z) = xyz/sqrt(4 - x2 - y2 - z2)
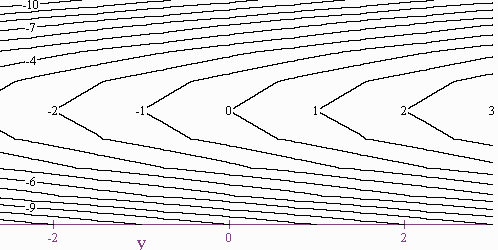
V. Level Curves
A map will be shown of the desolation wilderness that represents the function that maps a longitude and latitude to an altitude. We will investigate what the contour lines mean.
We will make our own contour map of the function
f(x,y) = y - x2 by setting constant values for z:
When z = 1, we have y = x2 + 1
When z = 2, we have y = x2 + 2