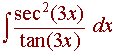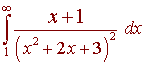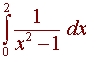Math 116 Practice Midterm 3
Problem 1
Integrate the following. If the integral is improper and diverges, state this. If the integral is improper and converges evaluate it.
Solution
We use partial fractions. We write
x -
1
A
B
=
+
x2 -
4
x - 2 x
+ 2
Clearing the denominators gives
x - 1 = A(x + 2) + B(x - 2)
Let x = 2: 1 = 4A A = 1/4
Let x = -2: -3 = -4B B = 3/4
We integrate
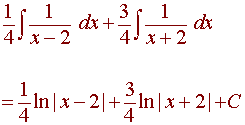
Solution
We use substitution
u = tan(3x) du = 3sec2(3x)dx 1/3 du = sec2(3x)dx
This gives us
![]()
Solution
Again we use substitution. We have
u = x2 + 2x + 3 du = (2x + 2)dx 1/2 du = (x + 1) dx
We change the limits to
u = 6 to u = infinity
This gives us
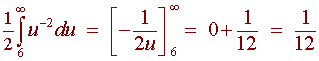
We use partial fractions here to get
1
A
B
=
+
x2 -
1
x - 1 x
+ 1
Clearing the denominators gives
1 = A(x + 1) + B(x - 1)
Let x = 1: 1 = 2A A = 1/2
Let x = -1: 1 = -2B B = -1/2
Notice that this is an improper integral since the function has an asymptote at x = 1. We need to write
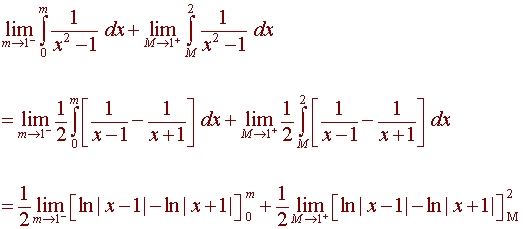
This integral diverges, since ln(0) is undefined.
The population P (in billions) of the world at time t years after 2,000 can be modeled by the equation
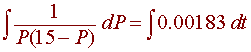
If in the year 2000, there were 6 billion people in the world. What will the population be in the year 2040?
Solution
We use partial fractions for the left hand side. We have
1
A B
=
+
P(15 -
P)
P 15 - P
Clearing the denominators gives
1 = A(15 - P) + BP
Let P = 0: 1 = 15A A = 1/15
Let x = 15: 1 = 15B B = 1/15
The left hand integral becomes
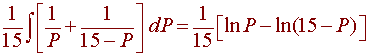
Notice that we used
u = 15 - P du = -dP dP = -du
for the second integral, hence the minus sign.
Integrating the right hand side and setting the equations equal, we get
1/15 [ln P - ln(15 - P)] = 0.00183t + C1
ln P - ln(15 - P) = 0.02745t + C We let C = 15C1
Using P(0) = 6 gives
ln 6 - ln 9 = C = ln(2/3)
We want the population in 2040, that is t = 40. We get
ln P - ln(15 - P) = (0.02745)(40) + ln2/3
ln[P/(15 - P] = 1.098 + ln(2/3) We used ln x - ln y = ln(x/y)
P
= e1.098 + ln(2/3) = 2
15 - P
P = 2(15 - P) = 30 - 2P
3P = 30
P = 10
The population is predicted to be 10 billion in 2040.
Consider the integral
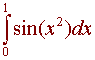
A. Use the Trapezoidal Rule to approximate this integral with n = 4.
Solution
We calculate
b - a 1 -
0 1
=
=
= 0.125
2n
2(4) 8
We have
x0 = 0 x1 = 0.25 x2 = 0.5 x3 = 0.75 x4 = 1
The integral is approximately equal to
0.125[sin(02) + 2sin(0.252) + 2sin(0.52) + 2sin(0.752) + sin(12)]
= 0.316
B. Use Simpson's Rule to approximate this integral with n = 4.
Solution
We calculate
b - a 1 -
0 1
=
=
= 0.083333
3n
3(4) 12
The integral is approximately equal to
0.083333[sin(02) + 4sin(0.252) + 2sin(0.52) + 4sin(0.752) + sin(12)]
= 0.310
C. Use the fact that |2cos(x2) - 4x2sin(x2)| < 3 to find a bound on the error from part A.
Solution
We find the second derivative of y = sin(x2). We have
y' = 2xcos(x2)
y'' = 2cos(x2) - 4x2sin(x2)
A bound for the error for the Trapezoidal Rule is
(b - a)3
(1 - 0)3
3
|E| <
(Max|f ''(x)|) <
(3) =
= .016
12n2
12(42)
192
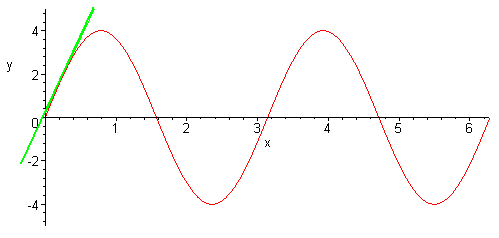
Consider the function
y = 4sin(2x)
A. Find the radian measure for the angle 15o.
Solution
We have
p
p
15
=
180 12
B. Without the use of a calculator determine the period an amplitude of the graph. Use this information to sketch the graph.
Solution
The amplitude is the coefficient in front of the sin, that is
A = 4
To find the period, we just write
2p
= p
2
The graph is shown below (along with the tangent line for part C)
C. Use part A. to determine the equation of the tangent line to the graph at the angle 15o. Then sketch this line on the graph.
Solution
We find the derivative
y' = 8cos(2x)
y '(p/12)
= 8cos(p/6)
= 4![]()
We have
y(p/12) = 4sin(p/6) = 2
We use the point slope form of the equation of the line.
y - 2 = 4![]() (x - p/12)
(x - p/12)
or
y =
4![]() (x - p/12)
+ 2
(x - p/12)
+ 2