Locating and Classifying Local Extrema
I. Quiz
II. Homework
III. Definition of Relative Max and Min
A function f(x,y) has a relative maximum at (a,b) if there is a delta neighborhood centered at (a,b) such that
f(a,b) > f(x,y)
similarly there is a relative minimum at (x,y) if
f(a,b) < f(x,y)
for all (x,y) in the delta neighborhood.
Theorem: If f(x,y) has a relative maximum or minimum then gradf = 0 there.
A visual proof will be given in class.
Example Let f(x,y) = x2 + xy - 2y + x - 1
then gradf = <2x + y + 1,x - 2> = 0
so that x - 2 = 0 or x = 2
Hence 2(2) + y + 1 = 0 so y = 5
A possible extrema is (2,-5)
Theorem (Second Derivative Test For Functions of Two Variables)
We call the matrix:
| fxx | fxy |
| fyx | fyy |
the hessian then the determinant is
D = fxxfyy - fxy2
then if gradf = 0 we have the following
| D | fxx | Type |
| >0 | >0 | Rel Min |
| >0 | <0 | Rel Max |
| <0 | any | Saddle |
| = 0 | any | Test Fails |
We will discus saddle points in class
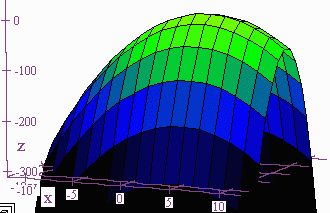
Example:
Let f(x,y) = -x2 - 5y2 + 8x - 10y - 13
then gradf = <-2x + 8,-10y - 10> = 0 at (4,-1)
we have fxx = -2, fyy = -10, and fxy = 0 Hence
D = (-2)(-10) - 0 > 0
so f has a relative maximum at (4,-1)
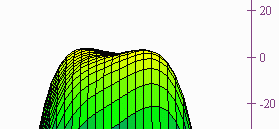
Example: Let
f(x,y) = 4xy - x4 - y4
The gradf = <4y - 4x3,4x - 4y3>
We solve:
4y - 4x3 = 0 so that y = x3
Hence 4x - 4(x3)3 = 0
x - x9 = 0 so that x = 1 or x = 0 or x = -1
this gives us the points (1,1), (0,0) and (-1,-1)
We have fxx = -12x2, fyy = -12y2, and fxy = 4
Hence D = 144x2y2 - 16
We write the table:
| Point | D | fxx | Type |
| (1,1) | 126 | -12 | Max |
| (0,0) | -16 | 0 | Saddle |
| (-1,-1) | 126 | -12 | Max |
IV. Minimizing Distance
Find the minimum distance from the point (2,1,4) to the plane
x + 2y + z = 5
Solution: We minimize the square of the distance:
D = (x - 2)2 + (y - 1)2 + (5 - x - 2y - 4)2
We take thr gradient and set it equal to 0:
<2(x - 2) - 2(5 - x - 2y - 4),2(y - 1) - 2(5 - x - 2y - 4)> = 0
so
2x - 4 - 10 + 2x + 4y + 8 = 0 and 2y - 2 - 10 + 2x + 4y + 8 = 0
4x + 4y - 6 = 0 and 2x + 6y - 4 = 0
2x + 2y - 3 = 0 and 2x + 6y - 4 = 0
subtracting the first from the second, we get:
4y - 1 = 0 so y = 1/4
Hence x = 7/4
Finally, we have
D = (7/4 - 2)2 + (1/4 - 1)2 + (5 - 7/4- 2(1/4) - 4)2
V. The Least Squares Regression Line
Example:
Suppose you have three points in the plane and wnat to find the line y = mx + b that is closest to the points. Then we wnat to minimize the sum of the squares of the distances, that is find m and b such that
d12 + d22 + d32 is minimum
We calculate
d12 + d22 + d32 = f = (y1 - (mx1+ b))2 + (y2 - (mx2+ b))2 + (y3 - (mx3+ b))2
To minimize we set
gradf = <fm, fb> = 0 (Notice that m and b are the variables)
fm = 2(y1 - (mx1+ b))(-x1) + 2(y2 - (mx2+ b))(-x2) + 2(y3 - (mx3+ b))(-x3) = 0
fb = -2(y1 - (mx1+ b)) - 2(y2 - (mx2+ b)) - 2(y3 - (mx3+ b)) = 0
We have
A) x1(y1 - (mx1+ b)) + x2(y2 - (mx2+ b)) + x3(y3 - (mx3+ b)) = 0
B) (y1 - (mx1+ b)) + (y2 - (mx2+ b)) + (y3 - (mx3+ b)) = 0
In sigma notation, we have
A) sum xiyi - m sum xi2 - b sum xi = 0
B) sum yi - m sum xi - nb = 0 where n = 3
We can solve to get
m = [n sum xiyi - sum xi sum yi ]/[n sum xi2 - (sum xi)2]
and b = 1/n( sum yi - msum xi )
Exercise: Find the equation of the regression line for
(3,2), (5,1) and (4,3)