Differentials
I. Quiz
II. Homework
III. The Total Differential
Definition: Let z = f(x,y) then the total differential for z is
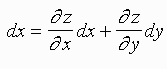
Example: For z = f(x,y) = x2 + xy
dz = (2x + y)dx + xdy
Exercise: Find dz if z = xsinycosy
IV. Application
In Chemistry we learn that PV = NRT, where NR is a constant. We can write:
T = PV/NR = kPV
Suppose at 25 degrees C gas is in an expanding cylinder of 55cc at a pressure of 3 atm. Also suppose that the pressure is increased by .1 atm and the volume is decreased by .05 cc. Then
dT = kPdV + kVdP approx k[(3)(-.05) + 50(.1)) = .35k
so that there is an increase on the temperature of about k(.35) degrees c
V. Error
Suppose that you measured the dimensions of a tin can bo be
h = 6 +- .1 inch and
r = 2 +- .05 inch
What is the approximate error in your measurement for the volume of the can?
Solution:
We have V = pi r2h
Hence the error can be approximated by
![]()
= 1.2 pi + .4 pi = 1.6 pi approx 5.0 cu inches
Hence the volume is
V = 75.4 +- 5 cu inches
VI. Differentiability
Theorem: If a function f(x,y) is differentiable at a point (a,b) then it is continuous at (a,b)
where differentiable means
Delta f(x,y) = fx(a,b)delta x + fy(a,b)deltay + e1deltax + e2deltay
where both e1 and e2 approach 0 as delta x and delta y approach 0. Furthermore if the partial derivatives are continuous then the function is differentiable.